Quick Answer
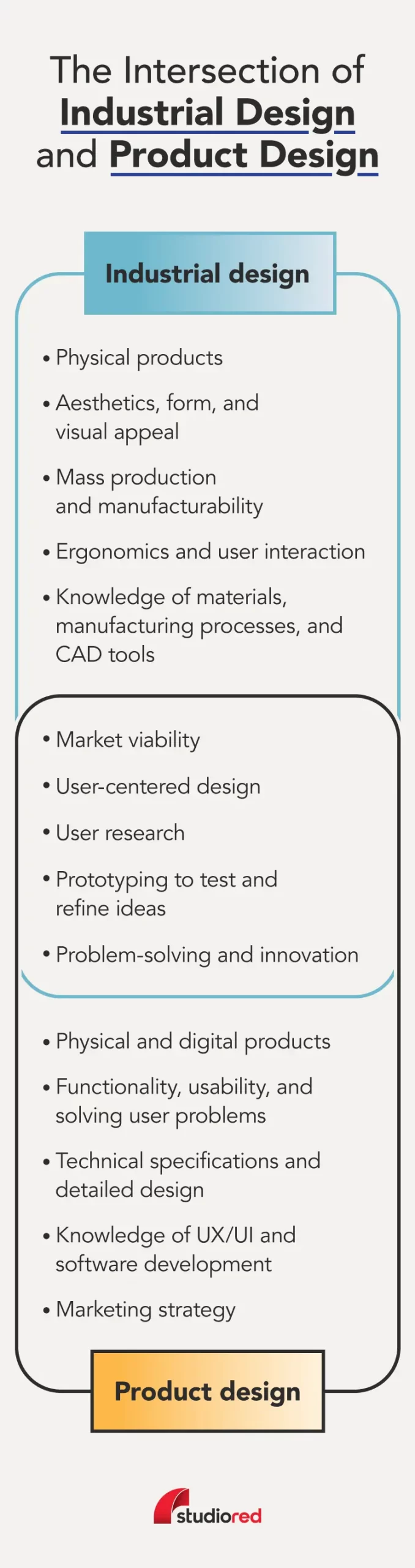
While the two terms are often used interchangeably, industrial design focuses on the form, aesthetics, ergonomics, and manufacturability of physical products, emphasizing the user experience and mass production. Product design includes both physical and digital products, with a strong focus on functionality, usability, and market viability.
Understanding the distinction between industrial design vs. product design helps narrow the focus when creating a new product. While both disciplines contribute to bringing a new product to life, they differ in scope, focus, and approach.
In this post, we’ll break down the key similarities and differences between industrial design and product design and how each discipline helps create innovative new products.
What Is Product Design?
Product design is a holistic process that encompasses the entire lifecycle of a physical or digital product, from ideation and development to launch and beyond. Product designers are concerned with understanding user needs, defining product strategy, and creating solutions that address those needs.
Historically, product design was primarily associated with the creation of physical objects, like appliances, furniture, or vehicles. However, as technology has advanced, the definition of “product” has expanded to include digital products like apps, software, and websites, revolutionizing the growing realm of IoT products.
This type of design focuses on strategic and tactical activities, like ideation and commercialization. Product designers also work closely with cross-functional teams, including engineers, marketers, and business stakeholders, to ensure the product is not only functional and user-friendly but also meets market demands and business objectives.
Some designated responsibilities of product designers often include:
- Functionality: Product designers look to solve specific user problems with an emphasis on how the product will function in the context of the user’s daily life.
- Digital prototypes: Both types of design use prototyping, but product designers use prototypes for digital products. These can include wireframes, clickthrough prototypes, and horizontal prototypes.
- Market feasibility analysis: Product designers assess whether the product is viable in the market, considering factors like cost, competition, and user demand.
What Is Industrial Design?
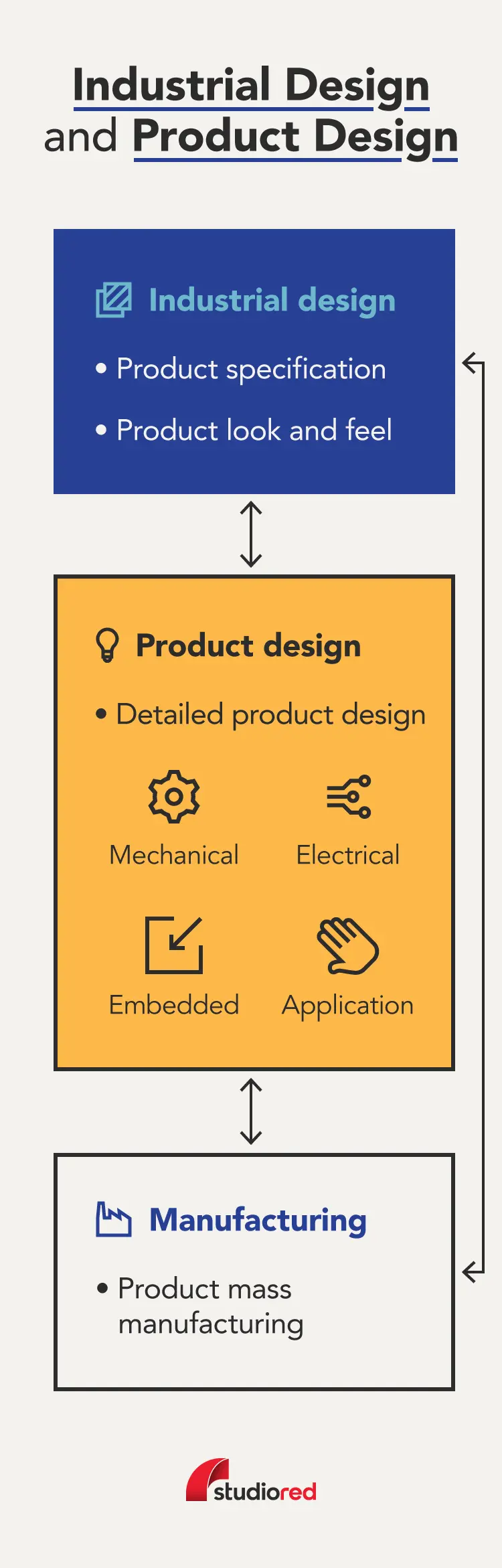
Industrial design is the art and science of creating physical products that are functional, aesthetically pleasing, and optimized for mass production. Industrial designers focus on how the products look, feel, and function in the hands of the user. They blend form and function to create solutions while focusing on human factors design elements.
Industrial product designers consider every aspect of a product, from its shape and materials to its ergonomics and usability. Some of their primary goals are to ensure the products are practical, durable, and aligned with the brand’s identity. Depending on the project, they may also collaborate with mechanical, electrical, and software engineers.
These designers create sketches, 3D models, and prototypes to test and refine their designs, ensuring the final product meets user expectations and manufacturing requirements. Sustainability is also a key consideration — designers are increasingly focused on using eco-friendly materials and processes to reduce environmental impact.
Some key activities of industrial designers include:
- Aesthetic design: They create visually appealing products that align with brand identity and user preferences.
- Ergonomics and usability: Industrial designers aim to create comfortable, intuitive, and easy-to-use products.
- Design for mass production: These designers create products that can be manufactured efficiently and at scale, considering factors like tooling, assembly processes, and cost optimization to ensure consistency and affordability in large-volume production.
- Prototyping and form function: They use different types of prototypes to test the product’s form, ergonomics, and overall design, focusing on the user experience.
Key Differences Between Industrial Design and Product Design
While industrial design and product design share common goals, they have some key differences. Understanding these distinctions can help designers choose the right discipline for their project’s needs.
Purpose
Product design focuses on developing solutions to specific user problems, emphasizing functionality, usability, and innovation. Product designers aim to create physical or digital products that meet user needs and stand out in the market.
On the other hand, industrial designers look for solutions while also focusing on the ability to mass-produce the product. Industrial designers also focus on a product’s aesthetics, ergonomics, and manufacturability, ensuring it’s functional and cost-effective to produce. Industrial design encompasses the entire journey from concept to the consumer.
Products
Industrial designers often focus on specialized, mass-produced physical products, like cars, appliances, and computers. These typically require a strong focus on user interaction and manufacturing efficiency.
Product design also develops everyday products but includes digital products like computer software and apps. These designers focus on information architecture and the UX and user interface (UI) design.
Technical Knowledge
Both product and industrial designers should have a general understanding of product development as a whole. For technical knowledge, industrial designers need to understand computer-aided drawing (CAD), materials science, ergonomics, and aspects of the manufacturing process like injection molding and tooling. Additionally, industrial designers may specialize in different forms of engineering, business operations, and creating prototypes.
Product designers also need to have a broad understanding of engineering principles, though they often specialize in digital engineering practices like software development and data analysis.
| Feature | Industrial Design | Product Design |
|---|---|---|
| Primary focus | Form, aesthetics, ergonomics, manufacturability of physical products | Functionality and usability for both physical and digital products |
| Scope | Focused on the physical product itself | Encompasses the entire product lifecycle |
| Deliverables | 3D models, prototypes, design specifications for manufacturing | Product strategy, user flows, wireframes, prototypes, technical specifications |
| Key skills | CAD software, materials knowledge, manufacturing processes | User research, UX design, product strategy, technical understanding |
Industrial Design and Product Design Similarities
While there are slight differences, industrial design and product design are more similar than they are different. Here are some of the most important commonalities:
- Problem-solving: Both involve identifying and solving problems related to product design and user experience.
- User-centered approach: Both disciplines prioritize understanding and meeting user needs.
- Iterative process: Both rely on iterative cycles of prototyping, testing, and refinement.
- Collaboration: Both often involve collaboration with cross-functional teams.
- Market viability: Industrial designers and product designers look to ensure products are something consumers want and will purchase.
By leveraging design thinking and iterative processes, both types of designers create user-centered solutions that make a meaningful impact. Their shared focus on problem-solving, excellent design, and user research highlights the significant crossover between these two fields.
Let the Experts Help With Your Next Project
Understanding the nuances of industrial design vs. product design is essential for creating innovative products that satisfy users and stand out in a competitive marketplace. Whether you’re focused on a product’s aesthetics and manufacturability or its functionality and technical details, both disciplines play a critical role in bringing your vision to life.
Here at StudioRed, we’re experts in the product design industry and take pride in helping our clients turn their product ideas into a reality. We’re here to help you create products that make an impact and drive success. If you’re ready to start your next project, contact us today to set up a consultation.





